Dogs with shallow, wide thoracic conformation have a short, round cardiac silhouette that, on the lateral radiograph, has a marked cranial inclination and a long area of sternal contact On the VentroDorsal or DorsoVentral views, the cardiac apex usually is located to the left of the midline and is often more difficult to identify because ofRADIOLOGY CHEST NORMAL RADIOGRAPHY Dr CAMUNGAO August 01, 19 1 AQUINO 3C R01 Introduction to Radiology Willhelm Conrad Roentgen () accidentally discovered Xrays in 15 Rontgen took this radiograph of his wife's left hand on December 22, 15 Xrays type of radiation called electromagnetic waves Xray imaging creates pictures of the inside of your bodyCT chest (pre and post contrast, arterial phase) is the ideal investigation, to determine presence of aortic intramural haematoma, true lumen and extent of dissection Appearance There is a true lumen and a false lumen, separated by an intimal flap
Q Tbn And9gctvmm0aifnsnulb4qkqzy7s6j0k3eduxlekyfj6cjkup59klby2 Usqp Cau
Radio thorax chat normal
Radio thorax chat normal-MidtermCHESTandABDOMINALPATHOLOGYRADIOREVIEWERpdf GAS PATTERN What is normal \u22 Stomach \u22 Almost always air in stomach \u22 Small bowel \u22CT (Cross sectional anatomy From Neck down towards Diaphragm) CT 1 Identify vascular structures Neck CT 2 Identify Trachea and Esophagus Entering Thorax CT 3 Identify vascular structures CT 4 Identify vascular structures Superior Mediastinum




Photo 1 Radiographie Thoracique D Un Chat Atteint D Un Pyothorax Download Scientific Diagram
Feb 18, 13 · The chest xray is the most frequently requested radiologic examination In fact every radiologst should be an expert in chest film reading The interpretation of a chest film requires the understanding of basic principles In this article we will focus on Normal anatomy and variants Systematic approach to the chest film using an insideoutFollowing are the causes of radioradial delay Normal anatomical variations Thoracic inlet syndrome eg cervical rib scalene syndrome Aneurysm of the aorta Presubclavlan coarctation Supravalvular aortic stenosis Pulseless disease (Takayasu's disease) Peripheral embolism Atherosclerosis of aorta4e année médecine – Rotation 3 – 15/16 ISM Copy Module de Cardiologie Interprétation d'une radiographie thoracique Télé thorax (TLT) de face se prend en inspiration forcée, les membres supérieurs en pronation forcée les paumes en dehors Télé thorax de profil se prend le coté malade sur la plaque, les bras levés
Aug 02, 07 · The axial image demonstrates that the opacity on the chest film is actually the liver As we follow the livercontour, there is this unusual shape (yellow arrow) There is discontinuity of the crus which is a nonspecific sign (small blue arrow) On the axial image there is indentation of the liver on the posterior side due to blood in the thoraxThe mean radiation dose to an adult from a chest radiograph is around 002 mSv (2 mrem) for a front view (PA, or posteroanterior) and 008 mSv (8 mrem) for a side view (LL, or laterolateral) Together, this corresponds to a background radiation equivalent time of about 10 daysNormal radiographic anatomy The entire thoracic radiograph should be evaluated, and it is important to develop a system so that every film is read in a consistent manner Evaluation of the thorax also includes the extrathoracic structures, such as chest wall, ribs, vertebra, sternum, diaphragm, and cranial abdomen (if visible) Chest wall
(a, b) Drawings (axial view) illustrate the normal thoracic CT anatomy at the level of the T2 (a) and T3 (b) vertebral bodies (c, d) Pancoast tumor in a 62yearold man with Horner syndrome (c) Axial CT scan demonstrates a Pancoast tumor in the left upper lobe (t) The mass is contiguous with the first rib in the area of the inferior cervicalNov 01, 00 · Findings at chest radiography may occasionally be normal despite the presence of diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage (, 32) Conclusions The systemic autoimmune diseases cause a variety of findings at chest radiography and highresolution CT Depending on the underlying autoimmune process, the pleura, pulmonary parenchyma, or airways may beThoracic CT A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses xrays to create crosssectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen CT stands for computerized tomography In this procedure, a thin Xray beam is rotated around the area of




œdeme Pulmonaire Cardiogenique Du Chat




Abdominal Ct Scans Definition Uses Picture And More
What is a CT scan of the thorax and upper abdomen?💎 NOUVELLES (17) 💎 Explications CLAIRES & ASTUCES Des Cours De Medecine ICI http//bitly/NewDrAstuceIl y a un cours que vous avezAug 01, 10 · The normal trachea at the thoracic inlet is between 15 and % of the thoracic inlet internal dimension as measured on the lateral radiograph For bulldogs and other brachycephalic breeds this measurement can approach 12% and still be considered normal Is the size of the trachea narrow (small luminal diameter)?



Radiographie Boules De Fourrure




Radiographie Clinique Veterinaire Saint Francois
In general, each lung has 10 segments the upper lobes contain 3 segments, the middle lobe / lingula 2 and the lower lobes 5 Bilaterally, the upper lobes have apical, posterior and anterior segments and the lower lobes superior (apical) and 4 basal segments (anterior, medial, posterior and lateral) With this basic symmetric anatomy sharedSep 01, 01 · (a, b) Drawings (axial view) illustrate the normal thoracic CT anatomy at the level of the T2 (a) and T3 (b) vertebral bodies (c, d) Pancoast tumor in a 62yearold man with Horner syndrome (c) Axial CT scan demonstrates a Pancoast tumor in the left upper lobe (t) The mass is contiguous with the first rib in the area of the inferior cervicalShoulder annotated xrays Case 84 Normal radiographic anatomy of the elbow Case 85 Elbow xray labeling questions Case 86 Carpal bones annotated xray Case 87 Wrist annotated carpal tunnel view



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson
Radiography of the thorax can be problematical due to difficulties eliminating movement blur resulting from breathing High output (high mA capability) Xray machines enable exposure times to be minimized, reducing the risk of movement blurNotice the cranial location of the thoracic limbs relative to the thoracic inlet Figure 2 (A) Dog in left lateral recumbency with thoracic limbs pulledFractures, penetrating wounds and neoplasia may cause displacement of or destruction of ribs The chest wall should be evaluated for changes in opacity (focal/diffuse opacities or lucencies) One of the biggest problems associated with interpretation of the thorax is associated with the normal chest wall, is skin folds




Hydatid Cysts Of The Liver Diagnosis Complications And Treatment Intechopen




Approaching The Patient With An Anterior Mediastinal Mass A Guide For Radiologists Sciencedirect
Oct 15, 17 · Radiology basics of chest CT anatomy with annotated coronal images and scrollable axial images to help medical students and junior doctors learning anatomyJan 10, 16 · Thoracic surface of the diaphragm (Atlas of Human Anatomy, 6th edition, Plate 191) Clinical Note Hiccups result from spasmodic contractions of the diaphragm and, if protracted, can have serious consequences (eg, cardiac dysrhythmias) The medical term for hiccups is singultusFeb 18, · This module of vetAnatomy is a basic atlas of normal imaging of anatomical feline radiology The 39 sampled xray images of healthy cats were performed by Susanne AEB Borofka (PhD dipl ECVDI, Utrecht, Netherland) Those images were categorized topographically into six chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, thorax and



2




Photo 1 Radiographie Thoracique D Un Chat Atteint D Un Pyothorax Download Scientific Diagram
In summary in a normal chest Xray, anatomical borders of the peripheral bronchi are invisible However, due to pathologic changes bronchi can sometimes be distinguished When the alveoli are filled with fluid (blood, pus, mucus, edema, cells) rather than air, a density difference develops between the alveoli and bronchiNov 10, · Chest radiotherapy side effects Chest radiotherapy includes radiotherapy to the breast, your chest wall (if you've had surgery to remove your breast) or to your chest itself This can include radiotherapy to the lungs or to the oesophagus (your food pipe or gullet) Side effects will depend on where you're having treatment toDec 24, 06 · The interpretation of interstitial lung diseases is based on the type of involvement of the secondary lobule The secondary lobule is the basic anatomic unit of pulmonary structure and function It is the smallest lung unit that is surrounded by connective tissue septa It measures about 12 cm and is made up of 515 pulmonary acini, that
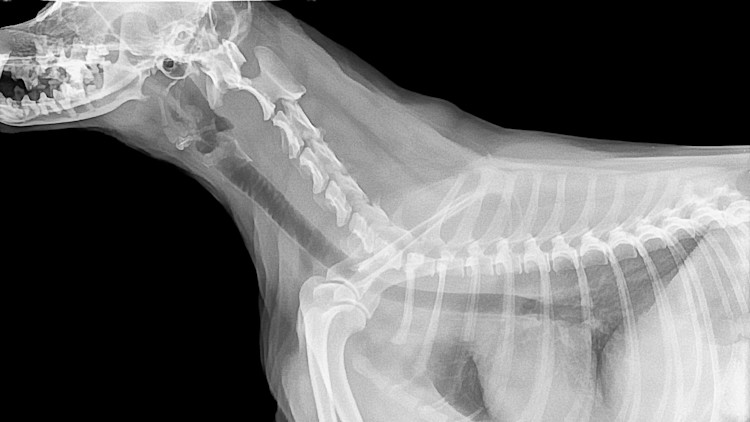



Dog X Ray Costs And How To Save Pawlicy Advisor




Abstractsthe 28th Annual Meetingnational Neurotrauma Symposiumparis Las Vegas Hotellas Vegas Nevadajune 14 17 10 Journal Of Neurotrauma
ImagingAnatomycom is an interactive atlas of normal imaging anatomy for the radiologist as well as a learning device for health professionals in general studying anatomy for any reason The atlas mimics a radiological workstation (PACS) and includes anatomy as it presents itself on plain film as well as on crosssectional studies with multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) and threedimensional90,000 US doctors in 147 specialties are here to answer your questions or offer you advice, prescriptions, and more Get help now Ask doctors free Personalized answers Free Talk to a doctor 24/7 visits $15 per month A 35yearold male asked(Slideset Comment examiner une radio du thorax ?) slide 15 Lorsque plusieurs tubulures centrales se chevauchent, il peut être plus difficile de déterminer leur emplacement Ce cliché d'une radiographie thoracique portative AP montre une tubulure dans la veine jugulaire interne droite et une tubulure dans la veine sous clavière droite




Imaging Anatomy



Normal Chest Radiography And Computed Tomography Radiology Key
SET 5 imaging tutorial #2 Thorax UQ Radiology 'how to' series Chest CT Introduction Forensic cases 19 Y4 Chest Imaging CT normal Krutines_kt Anatomy UQ Radiology 'how to' series Chest CT Neck, upper abdomen and bonesJun 10, 21 · Thoracic wall The first step in understanding thorax anatomy is to find out its boundaries The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature – all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage The thorax has two major openings the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracicUnder normal conditions, the pleural space contains a thin layer of fluid that prevents the two layers of the pleura from rubbing against each other When there's damage to the pleura, either due to lung disease or trauma to the chest wall, air from the outside or from the lungs can flow freely into the pleural space, but cannot leave



2
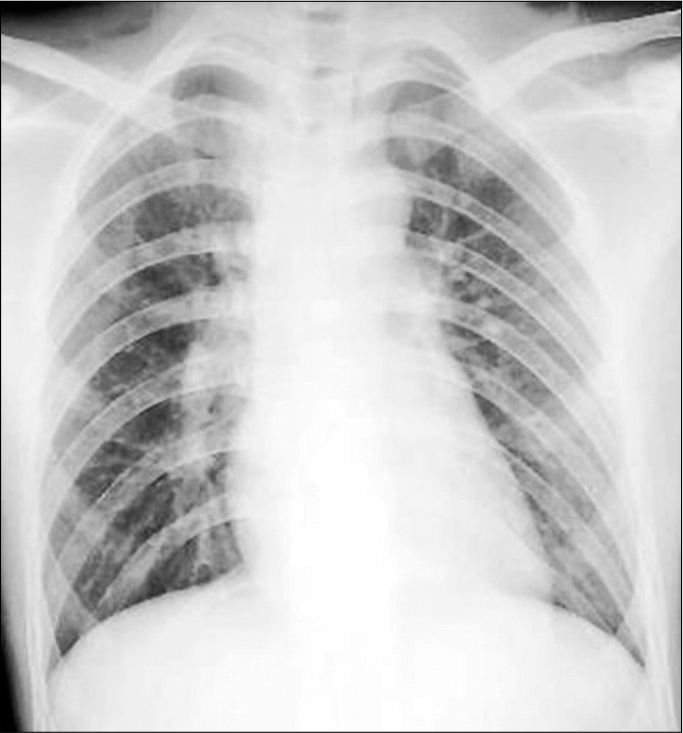



Delayed Definitive Treatment Of Life Threatening Neurosurgery Patient With Suspected Coronavirus Disease 19 Infection In The Midst Of Pandemic Report Of Two Cases Surgical Neurology International
To our present level of understanding and based on some 2,000 CT examinations of the thorax, we have described these pitfalls as they relate to the mediastinum, lung, pleura, and miscellaneous areas In general these pitfalls may be created by 1 Normal anatomic variation 2 The level of the CT slice and partial volume effect 3The normal thorax Some basic rules of thumb can be applied to most dog breeds The two breeds that will break all of the rules will be boxers and bulldogs The widest point of the cardiac silhouette on the lateral view in dogs should be between 25 to 35 intercostal spaces For a cat, on a lateral film, the widest point of the cardiacRadio du thorax Introduction Partie 1 Docteur SynapaseRéférences 1 https//radiopaediaorg2 http//wwwradiologyassistantnl




Radiographies Du Chat




You Don T Like Skydiving And I Don T Like Sex Why We Need To Talk About Asexuality The Correspondent
(A) Dog in right lateral recumbency with thoracic limbs pulled cranially See text for anatomic boundaries of collimated thorax (B) Right lateral thoracic radiograph of dog in Figure 2A;Here is my list of normal cases for reference Thorax Normal Thorax 1 6 yearold, male neutered, canine Samoyed Normal Thorax 2 7 yearold, male neutered, canine Weimaraner Normal Thorax 3 13 yearold, female neutered, canine Siberian Husky Normal Thorax 4 13 yearold, female neutered, canine Labrador RetrieverIt is a special Xray that allows us to create a series of detailed images of the inside of your chest and tummy area There is no other test that gives as much information on lung tissue The scanner consists of a doughnutshaped structure, about two feet thick with a hole in the centre



Differentiating Atypical Hemangiomas And Metastatic Vertebral Lesions The Role Of T1 Weighted Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Mri American Journal Of Neuroradiology



2
Aug 01, 10 · The normal thorax is well suited to radiographic evaluation because there is marked inherent contrast between the airfilled, fluidfilled, soft tissue, and bony structures that comprise the thoracic viscera and thoracic wall As has been stated before, at least 2 orthogonal views of the thorax are required for complete and accurate interpretation For routine evaluation of the thoraxA normal measurement is 0450 A measurement 050 is usually taken to be abnormal although some radiologists feel that measurements up to 055 are "borderline" The cardiothoracic ratioVET Talks is a project by the IVSA Standing Committee on Veterinary Education (SCoVE)This VET Talk is by Dr Pete Mantis, DVM, DipECVDI, FHEA, MRCVS, Senior




Que Peut On Voir Ne Peut On Pas Voir A L Examen Radiographique Clinique Veterinaire Mairie D Issy



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson
The chest or thorax is the region between the neck and diaphragm that encloses organs, such as the heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea, and thoracic diaphragm Computed tomography (CT) of the chest can detect pathology that may not show up on a conventional chest radiograph (1) This medical imaging tool uses special Xray equipment and computer technology to generate




Radiographies Du Chat




Pdf Imaging Diagnosis Intrapericardial Right Auricle Aneurysm In A Dog




Pyothorax Chez Un Chat Centre Hospitalier Clinique Veterinaire Cordeliers A Meaux 77




Neuroimaging Findings In Pediatric Genetic Skeletal Disorders A Review Wagner 17 Journal Of Neuroimaging Wiley Online Library




Pyothorax Chez Un Chat Centre Hospitalier Clinique Veterinaire Cordeliers A Meaux 77



The Normal Chest X Ray Reading Like The Pros Radiology Key
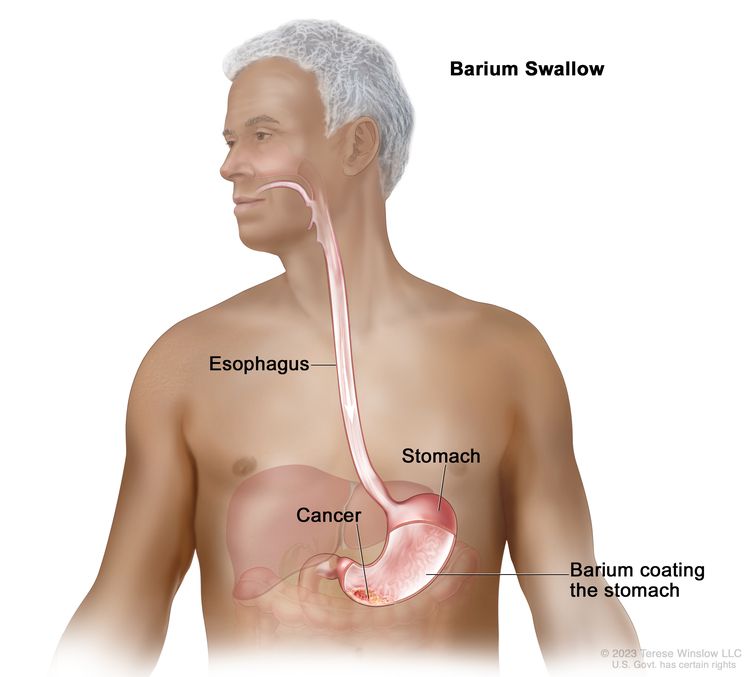



Gastric Cancer Treatment Pdq Patient Version National Cancer Institute




111 Vertebral Heart Size Vhs Dr Buchanan S Cardiology Library Vin




Radiographie Thoracique Images Normales Questions Et Images Fournises Par Dr Franck Durieux Dip Ecvdi Aquivet Radiographie Thoracique Images Normales Imagerie Diagnostique Et Outils Sessions Cardio Academy




Southern Regional Meeting 19 New Orleans La February 21 23 19 Journal Of Investigative Medicine



Dyspnee Chez Un Chat
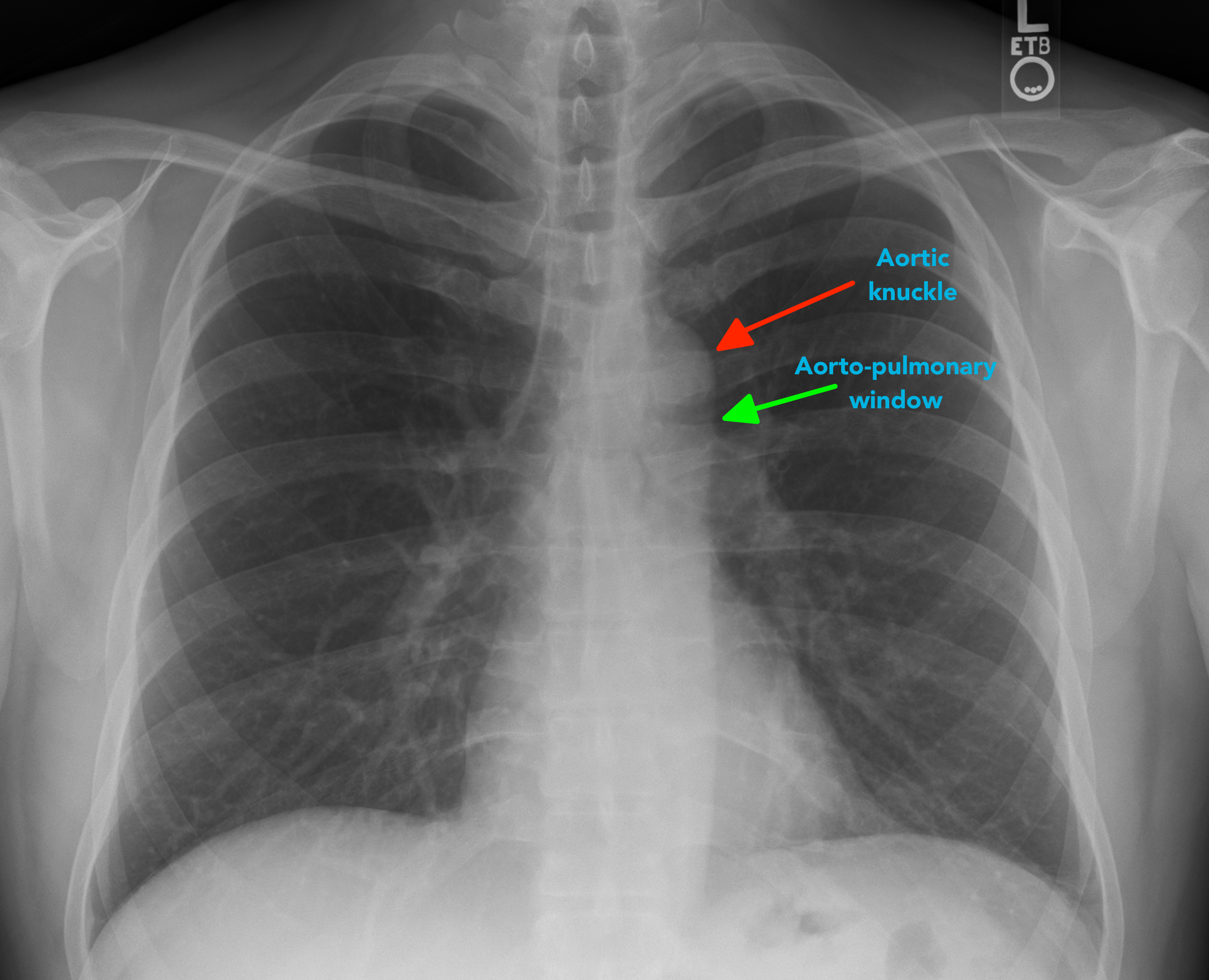



Chest X Ray Interpretation A Structured Approach Radiology Osce
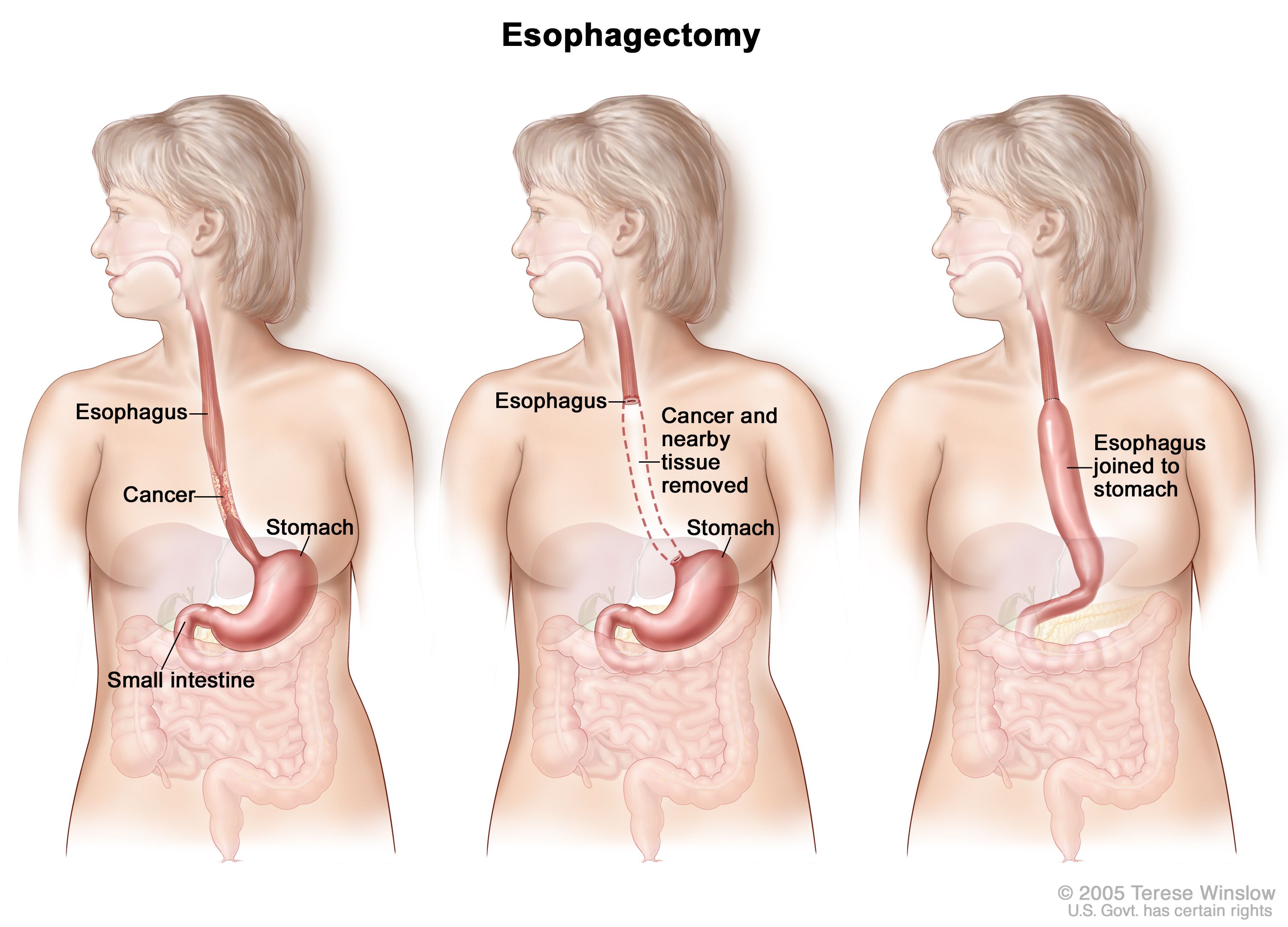



Esophageal Cancer Treatment Adult Pdq Patient Version National Cancer Institute




Radiographies Du Chat



Radiographie Boules De Fourrure




Normal Lung X Ray Vs Copd Perokok C



Chest Radiograph Resource Learn About Share And Discuss Chest Radiograph At Popflock Com



2




Radiographie Thoracique Images Normales Questions Et Images Fournises Par Dr Franck Durieux Dip Ecvdi Aquivet Radiographie Thoracique Images Normales Imagerie Diagnostique Et Outils Sessions Cardio Academy




Normal Chest Ct Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




Radiographie Imagerie




Used Satin Steel Metallic 18 Chevrolet Volt 5dr Hb Lt For Sale In Miami Fl Ju



Q Tbn And9gctvmm0aifnsnulb4qkqzy7s6j0k3eduxlekyfj6cjkup59klby2 Usqp Cau



Leviticus Cardio Achieves Successful Transcutaneous Coplanar Energy Transfer In Chronic Animal Model




What Do Normal Testosterone Levels Look Like Balance My Hormones




Radio Guided Robotic Parathyroidectomy For Mediastinal Parathyroid Gland




Collaborative Environment For Clinical Reasoning And Distance Learning Sessions Sciencedirect




Cabinet Veterinaire Sebastien Delgoffe Home Facebook




Excessive Sweating Questions About Miradry Treatment In Portland



Dyspnee Chez Un Chat




Dqzpsxwupqynzm




Pyothorax Chez Un Chat Centre Hospitalier Clinique Veterinaire Cordeliers A Meaux 77
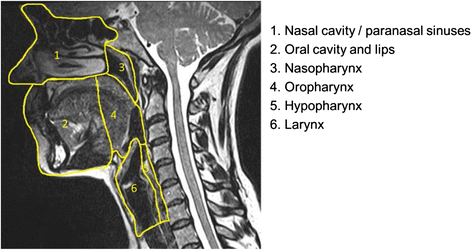



Cross Sectional Imaging In Cancers Of The Head And Neck How We Review And Report Cancer Imaging Full Text



2



Ce4rt Radiographic Positioning Of The Chest For X Ray Techs



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson




Pneumothorax Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Cardiothoracic Ratio Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Xazcoa144l9lym




Enhancement The Oxford Uehiro Centre For Practical Ethics




Chat De Thorax De Rayon X Photos Libres De Droits Et Gratuites De Dreamstime




Radiographie Imagerie




œdeme Pulmonaire Cardiogenique Du Chat




111 Vertebral Heart Size Vhs Dr Buchanan S Cardiology Library Vin



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson



Radiographie Boules De Fourrure




Chest X Ray Reading In Hindi Chest X Ray Results Explained Medical Guruji Youtube




Normal Chest X Ray Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson



Normal Chest Radiography And Computed Tomography Radiology Key



The Normal Chest X Ray Reading Like The Pros Radiology Key
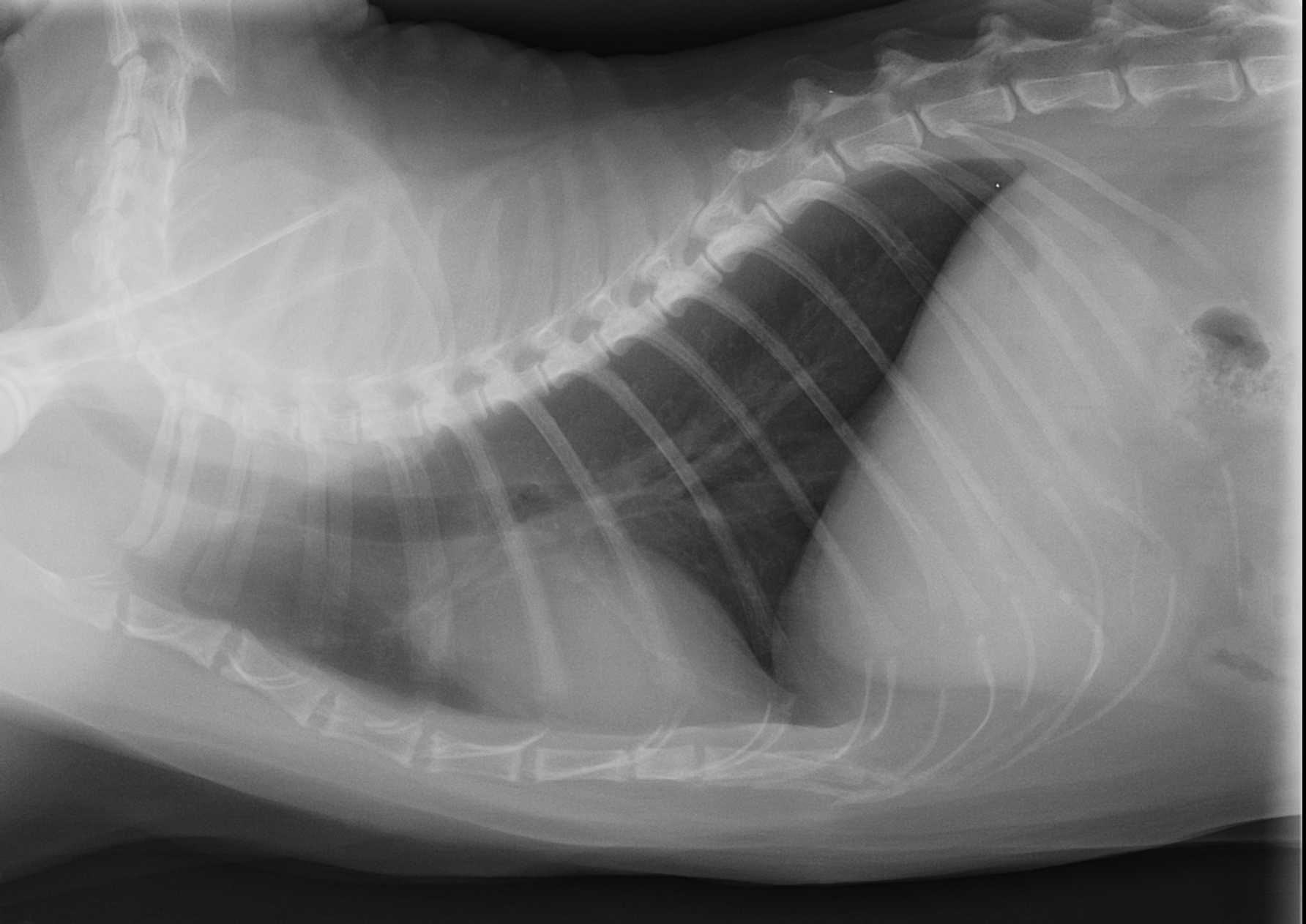



File Radiographie Thoracique Chez Un Chat Jpg Wikimedia Commons



Q Tbn And9gcsrjpzjootdh3q47ghw3pmq3to Dlnpstynscrsueewet6zj 2s Usqp Cau




Radiographies Du Chat




Radiographic Interpretation Of Thoracic Disease Vetfolio




Southern Regional Meeting 19 New Orleans La February 21 23 19 Journal Of Investigative Medicine




Normal Chest Imaging Examples Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Pneumothorax Et Pneumomediastins Spontanes Chez Un Chat Centre Hospitalier Clinique Veterinaire Cordeliers A Meaux 77




Radiographies Du Chat



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson



Radiographie Boules De Fourrure




Neuroimaging Findings In Pediatric Genetic Skeletal Disorders A Review Wagner 17 Journal Of Neuroimaging Wiley Online Library




Imaging Anatomy




New 22 Chevrolet Bolt Euv Lt Suv In Fremont 1c205 Sid Dillon



1




Interpreting Small Animal Thoracic Radiographs Clinician S Brief



They Ate What Pet X Ray Contest 12 Winners



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson
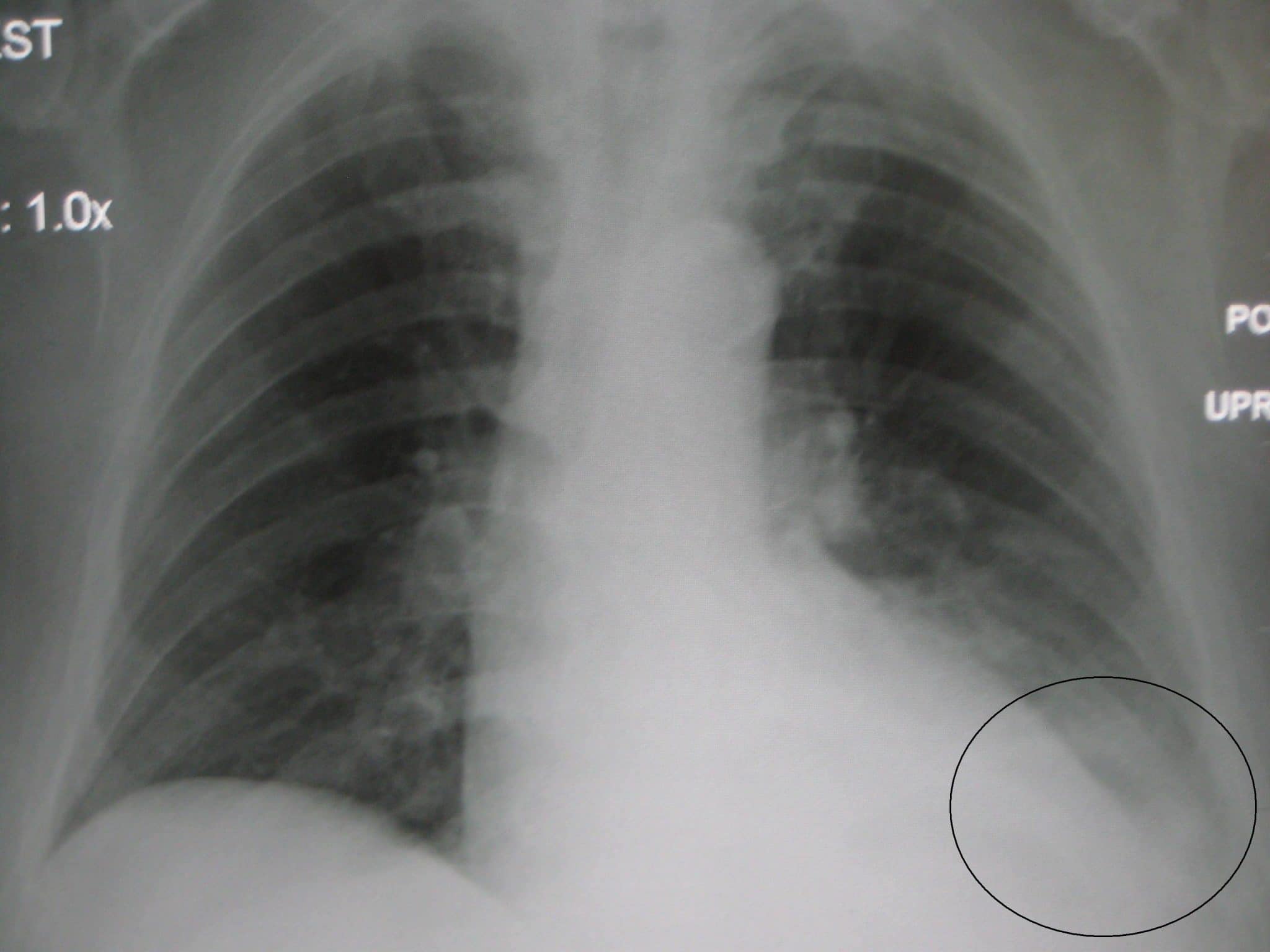



Chest X Ray Interpretation A Structured Approach Radiology Osce




Interpreting Small Animal Thoracic Radiographs Clinician S Brief




Radiographie Thoracique Images Normales Questions Et Images Fournises Par Dr Franck Durieux Dip Ecvdi Aquivet Radiographie Thoracique Images Normales Imagerie Diagnostique Et Outils Sessions Cardio Academy




Cardiothoracic Ratio Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




The Covid 19 Vaccine Arrives As New Cases Soar Kpbs Roundtable Kpbs




Cxr Images Royalty Free Stock Cxr Photos Pictures Depositphotos




Pyothorax Chez Un Chat Centre Hospitalier Clinique Veterinaire Cordeliers A Meaux 77



Radiographie Radioscopie Clinique Veterinaire Des Docteurs Martin Granel Beaufils Jumelle Calvisson




Rayons X Des Jambes Du Thorax Et La Tete Avant D Un Chat Normal Image Stock Image Du Humerus Radiologie




Pdf Imaging Adults On Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Ecmo



1




Chest X Ray Interpretation A Structured Approach Radiology Osce




Que Peut On Voir Ne Peut On Pas Voir A L Examen Radiographique Clinique Veterinaire Mairie D Issy



Aucun commentaire:
Publier un commentaire